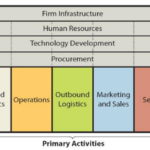
 Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis. Uber Value Chain Analysis Uber Primary Activities Uber Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service. Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services. Uber Operations Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. Business operations are divided into four reportable segments: 1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages: a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and…
Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis. Uber Value Chain Analysis Uber Primary Activities Uber Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service. Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services. Uber Operations Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. Business operations are divided into four reportable segments: 1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages: a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and…Uber Value Chain Analysis
Wednesday, July 21, 2021
Research Methodology
 Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis. Uber Value Chain Analysis Uber Primary Activities Uber Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service. Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services. Uber Operations Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. Business operations are divided into four reportable segments: 1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages: a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and…
Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis. Uber Value Chain Analysis Uber Primary Activities Uber Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service. Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services. Uber Operations Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. Business operations are divided into four reportable segments: 1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages: a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and…
0 Response to Uber Value Chain Analysis
Post a Comment