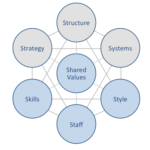
 IKEA McKinsey 7S model explains how individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. McKinsey 7S framework considers strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are accepted as soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values represent the core of IKEA McKinsey 7S framework. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with effects on their performance and ultimately on the bottom line for the business. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in IKEA 7S Model Strategy IKEA business strategy is based on the IKEA Concept, which is built upon the combination of function, quality, design and value – always with sustainability in mind. Moreover, the Swedish furniture chain offers cost advantage value for customers. Accordingly, IKEA business strategy involves offering increasing variety of products for the lowest prices. Regular engagement in new market development and benefiting from strategic alliances constitute additional pillars of IKEA business strategy. Structure IKEA organizational structure is unique and highly complex. The home improvement and furnishing chain maintains uniqueness and complexity its corporate structure in order to pay less taxes. The company can be divided into three large groups: franchise, range and supply and industry. Large scale of the business that integrates 11 franchisees operating in more than 500 locations in 63 countries[1] necessitates hierarchical organizational structure. Nevertheless, the Swedish furniture chain has proved to be successful in overcoming common weaknesses of hierarchical organizational structure such as high level of bureaucracy and lack of flexibility of the business. Systems IKEA business relies on a set of systems. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation…
IKEA McKinsey 7S model explains how individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. McKinsey 7S framework considers strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are accepted as soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values represent the core of IKEA McKinsey 7S framework. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with effects on their performance and ultimately on the bottom line for the business. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in IKEA 7S Model Strategy IKEA business strategy is based on the IKEA Concept, which is built upon the combination of function, quality, design and value – always with sustainability in mind. Moreover, the Swedish furniture chain offers cost advantage value for customers. Accordingly, IKEA business strategy involves offering increasing variety of products for the lowest prices. Regular engagement in new market development and benefiting from strategic alliances constitute additional pillars of IKEA business strategy. Structure IKEA organizational structure is unique and highly complex. The home improvement and furnishing chain maintains uniqueness and complexity its corporate structure in order to pay less taxes. The company can be divided into three large groups: franchise, range and supply and industry. Large scale of the business that integrates 11 franchisees operating in more than 500 locations in 63 countries[1] necessitates hierarchical organizational structure. Nevertheless, the Swedish furniture chain has proved to be successful in overcoming common weaknesses of hierarchical organizational structure such as high level of bureaucracy and lack of flexibility of the business. Systems IKEA business relies on a set of systems. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation…Specialized on Data processing, Data management Implementation plan, Data Collection tools - electronic and paper base, Data cleaning specifications, Data extraction, Data transformation, Data load, Analytical Datasets, and Data analysis. BJ Data Tech Solutions teaches on design and developing Electronic Data Collection Tools using CSPro, and STATA commands for data manipulation. Setting up Data Management systems using modern data technologies such as Relational Databases, C#, PHP and Android.
Tuesday, August 16, 2022
IKEA McKinsey 7S Model
 IKEA McKinsey 7S model explains how individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. McKinsey 7S framework considers strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are accepted as soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values represent the core of IKEA McKinsey 7S framework. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with effects on their performance and ultimately on the bottom line for the business. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in IKEA 7S Model Strategy IKEA business strategy is based on the IKEA Concept, which is built upon the combination of function, quality, design and value – always with sustainability in mind. Moreover, the Swedish furniture chain offers cost advantage value for customers. Accordingly, IKEA business strategy involves offering increasing variety of products for the lowest prices. Regular engagement in new market development and benefiting from strategic alliances constitute additional pillars of IKEA business strategy. Structure IKEA organizational structure is unique and highly complex. The home improvement and furnishing chain maintains uniqueness and complexity its corporate structure in order to pay less taxes. The company can be divided into three large groups: franchise, range and supply and industry. Large scale of the business that integrates 11 franchisees operating in more than 500 locations in 63 countries[1] necessitates hierarchical organizational structure. Nevertheless, the Swedish furniture chain has proved to be successful in overcoming common weaknesses of hierarchical organizational structure such as high level of bureaucracy and lack of flexibility of the business. Systems IKEA business relies on a set of systems. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation…
IKEA McKinsey 7S model explains how individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. McKinsey 7S framework considers strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are accepted as soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values represent the core of IKEA McKinsey 7S framework. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with effects on their performance and ultimately on the bottom line for the business. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in IKEA 7S Model Strategy IKEA business strategy is based on the IKEA Concept, which is built upon the combination of function, quality, design and value – always with sustainability in mind. Moreover, the Swedish furniture chain offers cost advantage value for customers. Accordingly, IKEA business strategy involves offering increasing variety of products for the lowest prices. Regular engagement in new market development and benefiting from strategic alliances constitute additional pillars of IKEA business strategy. Structure IKEA organizational structure is unique and highly complex. The home improvement and furnishing chain maintains uniqueness and complexity its corporate structure in order to pay less taxes. The company can be divided into three large groups: franchise, range and supply and industry. Large scale of the business that integrates 11 franchisees operating in more than 500 locations in 63 countries[1] necessitates hierarchical organizational structure. Nevertheless, the Swedish furniture chain has proved to be successful in overcoming common weaknesses of hierarchical organizational structure such as high level of bureaucracy and lack of flexibility of the business. Systems IKEA business relies on a set of systems. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation…
No comments:
Post a Comment